
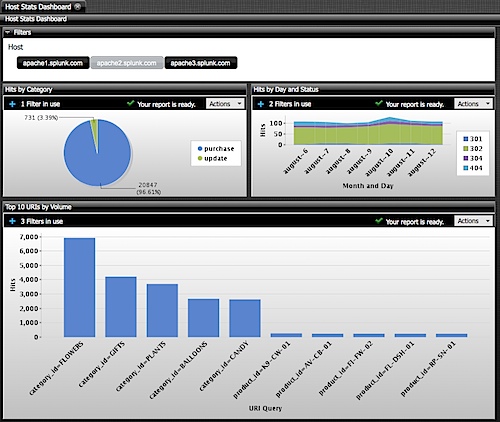
See Custom command functions in the SPL2 Search Reference to learn how to create a custom command function. Examples of built-in non-generating commands are stats, eval, and sort. A non-generating command function processes data that is piped in from generating commands or other non-generating commands.Examples of built-in generating commands are from, union, and search. A generating command function creates a set of events and is used as the first command in a search.There are two types of custom command functions: Use custom command functions to create a custom SPL2 command, A custom command function is a function that performs like a command. See Custom eval functions in the SPL2 Search Reference to learn how to create a custom function. As part of evaluation expressions with other commands.Custom functions provide a structured way to share and reuse blocks of SPL2. You can create your own custom eval functions to extend SPL2. See Overview of SPL2 dataset functions in the SPL2 Search Reference.
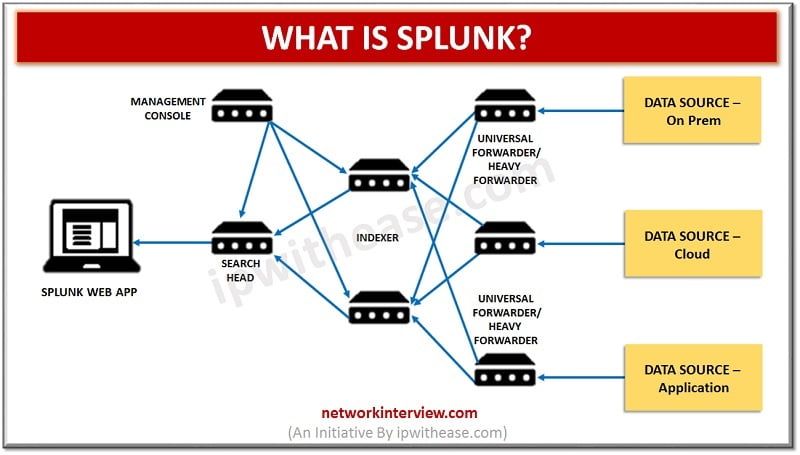
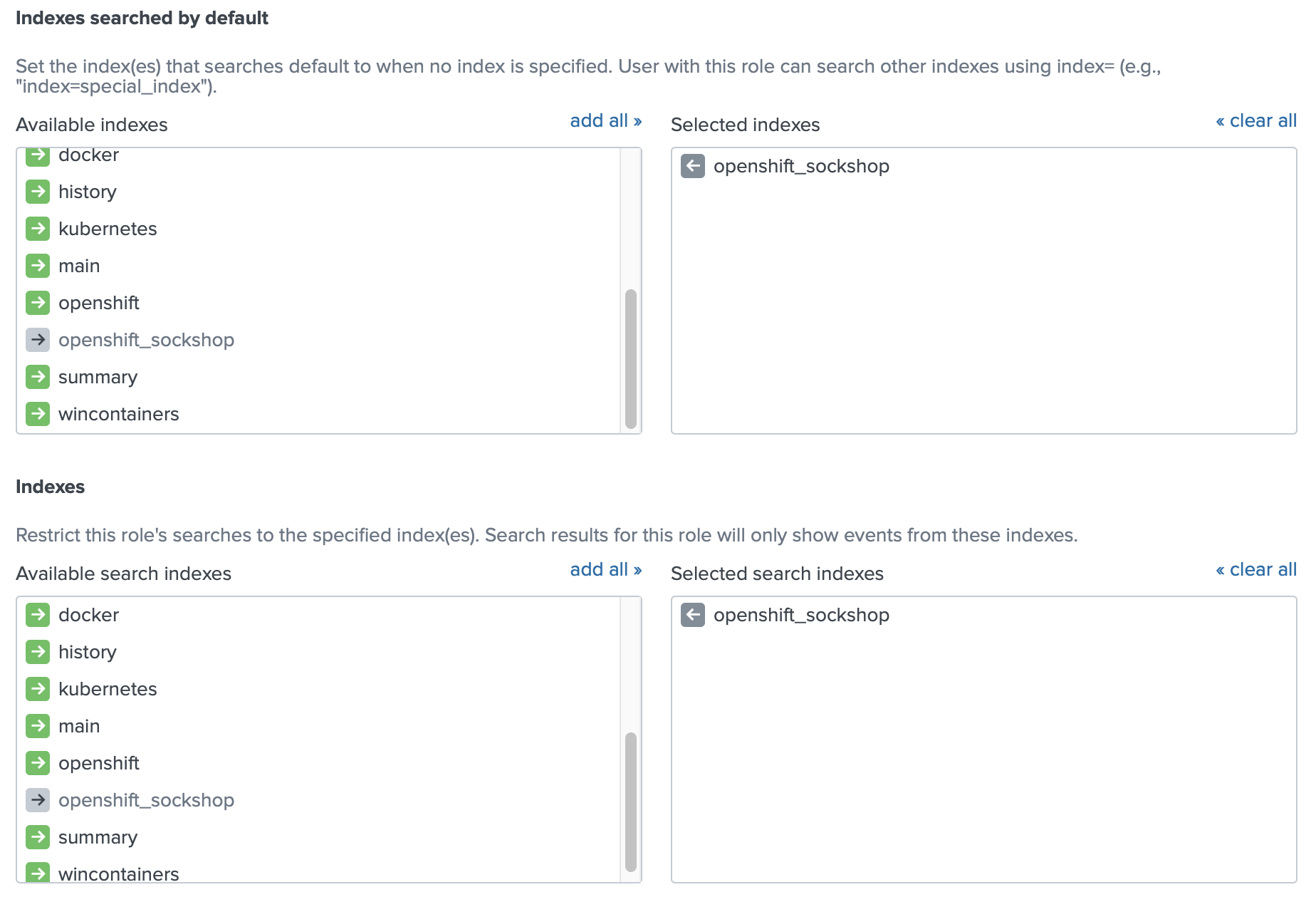
You can use dataset functions with any generating command, such as the from, join, and union commands. See Overview of SPL2 stats and chart functions in the SPL2 Search Reference.ĭataset functions are functions that create events to form a dataset. You can use the statistical and charting functions with the The only way I could validate logs were making it to the Splunk server was with a packet capture. Use statistical and charting functions to generate a calculation, such as an average or percentage, based on the field values in your events. I followed the documentation on how to connect an F5 load-balancer, Cisco ASA, and Checkpoint Firewall. See Overview of SPL2 eval functions in the SPL2 Search Reference. See Types of expressions for information about the expressions that you can use in evaluation functions.
With other commands that accept expressions.In the WHERE and SELECT clauses of the from command.Use evaluation functions to evaluate an expression, based on your events, and return a result. Functions that accept numbers can accept either a literal number or a field name where the field values are numbers. You can also create custom functions if the built-in functions don't meet your specific needs.įunctions that accept strings can accept either a literal string or a field name where the field values are strings. SPL2 includes a large set of built-in functions. Functions accept inputs in the form of parameters and return a value. Functions are used with commands to perform a specific task, such as a calculation, comparison, evaluation, or transformation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
